Behandlungsmöglichkeiten
The NeuroGyn patented GNS Therapy ®
Pelvic organ dysfunctions are complex and difficult to treat. These conditions affect a substantial portion of the population, especially with increasing age. Current stimulation therapies (Interstim therapy, Medtronic) have found no resonance in gynecology, while the vast majority of patients 70-80% are women. Further factors such as unfavorable reimbursement scenario (cost for neuroprothesis!) and lack of trained professionals are likely to pose a deterrents hampering market growth. Fro technical point o view, all techniques of implantation within the pelvic cavity are difficult to be reproduced by most gynecologists, while all techniques of implantation outside the protection of the pelvic cavity expose patients for lead migration and breakage. In this context, the stimulation of the genital nerves – GNS therapy – or more precisely of the dorsal nerve of the penis/clitoris (DNP) emerges as a very attractive alternative to other neuromodulative therapies that might result in great outcomes for controlling urinary, fecal and sexual disorders (see: Possover M. Minimally Invasive Two-passage Electrical Genital Nerve Stimulation: A Human cadaver study of a technique. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 2023 Jun;30(6):480-485. Doi: 10.1016/j.mig.2023.02.024).
GNS is the first method of stimulating pelvic nerves that does not require an operative test phase.
In neuromodulative therapies for pelvic organs dysfunctions, a temporary lead-electrode is traditionally placed surgically under general anesthesia to the nerves, in order to test the effectiveness of electrical stimulation on the symptoms. This test phase allows clinicians to judge how much a patient will benefit or not from a permanent neuroprothesis. In contrast to all current techniques , the GNS is the only one which does not require any surgical test-phase: Because part of the DGN lies superficially to the skin outside the pelvis, this nerve can be stimulated using surface adhesive electrodes attached to the overlying skin close to the vulva or the penis (Fig 1). Stimulation is simply achieved using a battery powered hand-held stimulator.
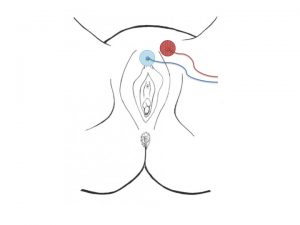
Fig. 1: placement of surface skin electrodes for DNP-stimulation
The effect of the stimulation can be tested by the patient in their daily, home and professional environment, or at the practice under urodynamic testing, or if required other electrophysiological testing.
The GNS-therapy is a procedure for implantation a permanent lead-electrode reproducible by every gynecologist trained in TVT procedure – one of the most frequent performed procedure in gynecology to treat stress urinay incontinence in women.
Studies using stimulation of the DGN have been performed more than three decades; the main issue still remains, the way of stimulation the nerve on long time. Stimulation using surface skin electrodes is limited for permanent stimulation, due to intolerance to required high stimulation amplitude. Surface electrodes have additional limitations such as difficulties in proper daily placement and issues related to hygiene as well as a lack of acceptance in some patients. Implanted electrodes are definitively more suitable. However, implanted electrodes in the penis or near the clitoris, must endure the mechanical stress of penile erections and external pressure, carrying the risk of the cable/electrode breaking or being and dislocated.
Thus the challenge was to develop an implantation technique that is minimally invasive, which allows :
– the implantation lead electrode in direct contact to the dorsal genital nerve outside the pelvis
– the implantation of the pacemaker within the protection of the pelvis (an implantation of the generator at the genital level is impossible!),
– the protection of electrode’s cable on its path to the pacemaker from external trauma (risk of cable rupture when it passes under the skin).
The GNS procedure offer all these advantages: lead implantation is obtained very easy by a vaginal retropubic approach using the „Curve Applicator, NeuroGyn AG, the cable is protected by the pubic bone while the generator is implanted through a suprapubic mini-laparotomy behind the pubic bone.
Pelvic organs dysfunctions are very common conditions that affects a very large part of the general population. First-line conservative treatments do not always lead to sufficient improvement of the complaints and/or are often associated with disabling adverse effects (60% discontinuation). Neuromodulation has emerged as an alternative for treatment for pelvic organs dysfunctions. One and the current only option is the InterStim Therapy (Medtronic). Increasing cognizance regarding these devices is expected to serve as a market driver leading to an increase in the market share of these devices. This „InterStim“ is FDA-approved since 1997 for OAB and since 1999 for urinary retention and urgency, but only about 100,000 people worldwide have received InterStim® Therapy. This number is very disappointing when compared to the numbers of patients who may benefit from neuromodulation – a clear evidence of inadequacy of Interstim treatment. The main reason for this is that InterStim is absolutely unsuitable for surgical techniques in gynaecology and present a high rate for secondary lead migration, infection and treatment failure. Also factors such as unfavorable reimbursement scenario and lack of trained professionals are likely to pose as deterrents hampering market growth.
It is more than necessary to introduce neuromodulation to the pelvic nerves with main focus in Gynecology – this is the right time now! The Global Women Health Market is simply waiting to be conquered! Whether the „neuromodulation market“ has already perceived the potential of NeuroGyn is unknown to us, but the „medical community“ has clearly perceived it.
GNS-Therapy is a simple and minimally-invasive surgical procedure, which allows gynecologists to monitor their patients themselves. Therefore GNS will make a urge difference in Women Health once we consider on one side than 2/3 of all these conditions occur by women (about 400 Million in industrialized countries) and on the other side the urge number of gynecologists around the world: The WHO estimated about 25 to 35 Gynecocologist per 100 000 population, with a demand growing by 6% during the next decade.
GNS then offers tremendous advantages for patients, insurers and gynaecologists alike:
- For patients: The GNS-therapy is the first therapeutic option that allows the evaluation of neuromodulation without the need for a surgical test phase. The test-phase is done by the patient him/herself at home/work by simply using surface skin adhesive electrodes. The final implantation of the neuroprothesis – GNS-therapy – required only a local anesthesia, take only 15 minutes, can be done in ambulatory sector and is completely reversible (the neuroprothesis can be removed easily under local anesthesia, at any time; in Interstim therapy, the implantation is not reversible!).
- For health insurers: compared to classical techniques for pelvic nerves stimulation, the GNS-therapy enables a massive cost reduction of at least 60-70% of global costs comparing to competitors. We have also to consider that statistically 30-40% of the patients will not pass the test-phase. The patients are then not suitable for permanent neuromodulation and the costs of the test-phase have be done for “nothing”. The final implantation of the neuroprothesis for permanent neuromodulation is performed in local anesthesia, take <15min and on an outpatient basis.
- For physicians/gynecologists: the GNS-therapy finally opens the doors for neuromodulative treatments pelvic physicians, especially for Gynecologists. The GNS surgical technique is almost exactly the same kind of intervention as the TVT technique, which almost any operating gynecologist performs for the treatment of urinary stress incontinence.
All patents as well for the indications for the GNS, the GNS procedure itself, as the Neurogyn neuroprosthesis (pacemaker) and the surgical applicator belong to Neurogyn AG
Main indications for GNS therapy
Overactive bladder (OAB)
OAB is a urological condition defined by a frequent and unstoppable feeling of needing to urinate to a degree that it negatively affects a person’s life (every 10-30 minutes, both day and night). OAB is among the most common disorders among older adults, affecting approximately 16.0% of men and 16.9% of women in the US (127 Million People in US and Europe). The overall cost associated with OAB is > $9 billion (2000 US$), including $78 million for diagnosis and $2.79 billion for treatment, to be added to consequence costs, such as of $1.56 billion for routine care, $3.88 billion for health-related consequences, and to $841 million in lost productivity at work. If the estimated $2.9 billion for the institutional cost of OAB were added, the total cost for OAB was > $12 billion annually in the US. Thus, the total costs for OAB were of the same magnitude as those for breast cancer ($12.7 billion) and osteoporosis ($13.8 billion).
Urinary incontinence (UI)
UI is defined as an involuntary loss of urine. The US Department of Health and Human Services estimates that approximately 13 million Americans suffer from UI. UI is an underdiagnosed and underreported problem that increases with age, affecting 50-84% of the elderly in long-term care facilities. The economic burden of UIin the US is enormous, approximately $76.2 billion dollars in 2015.
Fecal incontinence (FI)
FI is defined by the unintentional loss of solid/liquid stool and gas. FI has a prevalence that ranges from 7 to 15% in community-dwelling men and women. Based on a review of approximately 3,500 surgeries performed over a 5-year interval for FI in Europe, the total hospital costs were $34.1 million (adjusted to 2012).
Uro-Genital Pain (Vulvodynia, Coccygodynia, chr. Prostatitis, IC..)
6.9 Million patients in the US suffer from Uro-Genital pain and are refractory to medication, of which only approximately 25000 patients are treated currently with neurostimulation.
Erectile Dysfunctions (ED)
ED is a common problem in primary care and currently affects > 150 million men worldwide, with a projected prevalence increase to 322 million men by the year 2025. A report from the UK estimated the total economic burden of ED at £53 million annually in terms of direct costs and lost productivity.